HSK (Level II)
The HSK (Level II) assesses test takers’ abilities in the application of daily Chinese communication. It is the counterpart of the level II of the Chinese Language Proficiency Scales for Speakers of Other Language and the A2 Level of the Common European Framework of Reference (CEF). Test takers who are able to pass the HSK (Level II) have an excellent grasp of basic Chinese and can communicate in simple and routine tasks requiring a simple and direct exchange of information on familiar and routine matters.
- Test Target
The HSK (Level II) in intended for students who have studied Chinese for two semesters (an academic year), with 2-3 class hours in each week. These students have mastered 300 commonly used words and related grammar patterns.
2、Test Content
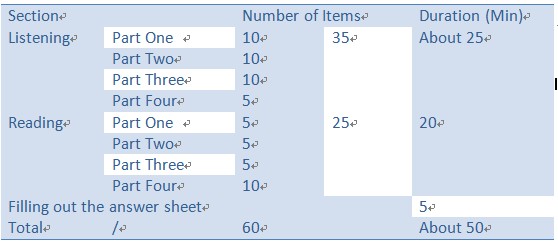
The HSK (Level II) test is made up of listening comprehension and reading comprehension sections and contains a total of 60 items.
| Section | Number of Items | Duration (Min) | ||
| Listening | Part One | 10 | 35 | About 25 |
| Part Two | 10 | |||
| Part Three | 10 | |||
| Part Four | 5 | |||
| Reading | Part One | 5 | 25 | 20 |
| Part Two | 5 | |||
| Part Three | 5 | |||
| Part Four | 10 | |||
| Filling out the answer sheet | 5 | |||
| Total | / | 60 | About 50 | |
The test will last for a total of 55 minutes (including 5 minutes in which the test takers fill in personal information).
- Listening
- There are 10 items in Part One. The recording of each item will be played twice. A sentence and a picture will be provided with each item. The test takers should make a true-or-false judgment based on what they hear.
- There are 10 items in Part Two. The recording of each item will be played twice. For each item, a dialogue and several pictures will be provided. The test takers should select the appropriate answer based on what they hear.
Compare to the HSK (Level I), the difficulty of the HSK (Level II) is slightly higher. The HSK (Level II) directly assesses the students’ abilities of identifying and judging of sentences and dialogues, skipping the assessment of single word’s pronunciation and understanding. The requirement for longer length of memory and comprehension is along with the longer record of listening material. Therefore, besides the consolidation of Pinyin pronunciation and semantics, the key point of this period of training is to enhance the students’ comprehension of long sentences through the possible pedagogies such as long-sentence making and long-sentence speaking.
- There are 10 items in Part Three. The recording of each item will be played twice. Each item consists of a dialogue between two persons with a third person asking a question related to the content. There will be three possible answers on the test paper from which the test takers can select the correct one based on the passage.
- There are 5 items in Part Four. The recording of each item will be played twice. Each item consists of a four-to-five-sentence dialogue between two persons with a third person will asking a question at the end of the passage. There will be three possible answers on the test paper from which the test takers can select the correct one based on what they hear in the passage.
Part Three and Part Four pay emphasis on test takers’ master of grammar. Compared to the HSK (Level I), the difficulty of HSK (Level II) is increased by the length and complexity of the listening material. It is proved for the second time that the key point of HSK (Level II) training is the students’ ability of listening, reading and comprehension of long, complex sentences.
- Reading
- There are 5 items in Part One. Several pictures will be shown on the test paper. For each item, a sentence will be provided. The test takers should choose corresponding pictures based on the sentence.
The HSK (Level II) is different from the HSK (Level I) because of the greatly raised importance on grammar master. Thus, there is only one item testing the semantics alone. The key point of HSK (Level II) reading comprehension training should focus on grammatical knowledge.
- There are 5 items in Part Two. For each item, one or two sentences will be provided in which one word is missing. The test takers should select one of the words from the answer section to fill in the blank.
- There are 5 items in Part Three. For each item, two sentences will be provided. The test takers should judge whether or not the second sentence is consistent with the first one.
Part Two and Part Three pay emphasis on the assessment of Chinese grammar with small percentage of semantic assessment. Part Two assesses students’ master of different properties of vocabulary and the collocation. The test takers are required to know the property of commonly used words and the basic syntax. Part Three assesses the collocation of specific words and specific syntax patterns, that is, Part Three is the combined assessment of semantics and grammar. The key training point of is the accurate identifying and understanding of some special characters or words. The teacher should explain clearly the different practical application of many confusable characters or words that seem to have similar meaning, which will help students to handle this section.
- There are 10 items in Part Four. In this section, 20 sentences will be provided. The test takers will be asked to find the correlations between the sentences.
Part Four reading comprehension is still the assessment of pragmatics. The test takers are required to judge the meaning, function and relation of sentences under the general context of the situational dialogue. Therefore, the teacher should encourage students to speak more and think more during the training of this section.
All items on HSK test paper are shown in Pinyin.
The key point of HSK (Level II) is still on practical dialogues and the marking of Pinyin is also assessed.
3、Results Certificate
For the HSK (Level II), three results will be provided including listening, reading and total. The test takers must score at least 120 points total to be considered passing.
| Max Score | Your Score | |
| Listening | 100 | |
| Reading | 100 | |
| Total | 200 |
Summary:
The HSK (Level II) is slightly more difficult than HSK (Level I) as to the in-depth grammar and complex dialogues. Thus, when preparing for the HSK (Level II), besides the basic knowledge of Pinyin, the main point should be put on the education of in-depth pragmatics and grammar.
